Key points:
- It is most important tool in a procedural programming.
- A function can be defined as a block of statements which is used to perform any particular task according to requirements.
- The main objective of function is to reduce the complexity of programs.
- In this case a large program can be divided into multiple parts, that part is called function or module.
There are some advantages of function :-
- We can create user friendly program with the help of function. In this case the user can create separate function for each module according to requirements.
- It provides reusability. It means a written source code can be saved multiple times.
- It provides extendibility . It means a program can be modified and extended in future.
- It reduces the complexity of programs.
- It provides readability. It means function oriented program is more readable rather than non function oriented programs.
- Function creates user friendly program because debugging process is easy.
Types of function :-
There are two types of function :
 |
| Types of function in C |
- Predefined function (inbuilt function)
- User defined function ( customized function )
Predefind function :-
This type of function is already defined in programming language. We cannot change the behaviour of function.
example:-
printf() , scanf() , clrcr() , getch() , strlen() , etc.
User defined function :-
This type of function is created with the help of user according to requirements.
example:-
findarea() , findfact() , even() , etc.
Function prototype :-
- It represents architechture of function.
- It must be required if main function is defined before user defined function.
- It must be written after declaration of header file.
example:-
#include<stdio.h>
void findsum();
void main()
{
findsum();
}
void findsum()
{
statements;
}
How to call a function :-
syntax :-
function name();
example :-
void main()
{
findsum();
}
Function architecture / pattern :-
It represents type of function as return type , non-return type , parameterised or non-parameterised.
There are four architecture of function :-
- A function with no return type and no parameter / argument.
- A function with return type but no parameter / arguments.
- A function with no return type but with parameter / arguments.
- A function with return type and with parameter / arguments.
How to create user defined function :-
1. function with no return type and no parameter
syntax :-
void <function name> ()
{
block of stmts;
}
 |
| function with no return type and no parameter syntax |
example :-
void display()
{
printf( “ hello” );
}
2. Function with return type but no parameter
syntax:-
<data type>
<function name> ()
{
block of stmts;
}
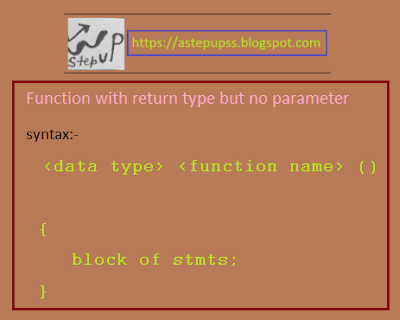 |
| function with return type but no parameter syntax |
example:-
int findadd()
{
int a = 10, b = 20 ;
add = a + b ;
return (add) ;
}
Parameter:-
Parameter is a special variable which can be supplied during a function and calling a function.
There are two types of parameter:
1. formal parameter :- Those parameters which are supplied during creating a function called formal parameter . It is treated as local variable.
2. actual parameter :- Those parameters which are supplied during calling a function. It is also called as argument.
3. A function with no return type but with parameter
syntax:-
void <function name> ( <data type> <parameter
1>, ..)
{
block of stmts;
}
 |
| function with no return type but with parameter syntax |
example:-
void findadd( int a,
int b)
{
int add ;
add = a + b;
printf( “ addition =
%d “, add);
}
4. A function witth return type and with parameter
syntax:-
<data type>
< function name > ( parameter list )
{
block of stmts;
return (variable);
}
 |
| function with return type and with parameter syntax |
P.example:- Program to input any no. after that find factorial value using function.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void findfact()
{
int a, fact=1 , i ;
printf( “ enter the
no “ );
scanf( “ %d “, &a
);
for ( i = 1 ; i
<= a ; i ++ )
{
if( a % i == 0 )
fact = fact * i ;
}
printf( “ factorial =
%d “, fact );
}
void main()
{
clrscr ();
findfact ();
getch ();
}
We practice more program on this topic on the next blog.

No comments:
Post a Comment